Explore, Wonder, Experience our World
|
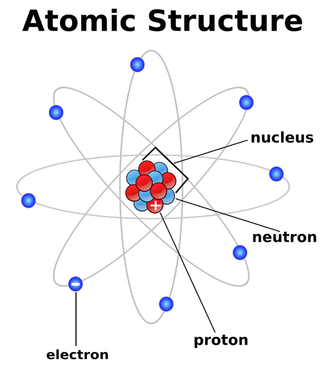
So what is an atom made of? The middle of each atom is a "nucleus." The nucleus contains tiny particles called protons (which are positively charged) and neutrons (which neutral or no charge). Orbiting around the nucleus are even smaller particles called electrons (which are negatively charged). |
So where does energy come from? First, we will need to learn a few things about the smallest building material in our world.
Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are nature's building blocks. Different types of atoms are called elements. Atoms join together in many different combinations to form molecules. This creates all the materials you see on Earth. |
|
|
|

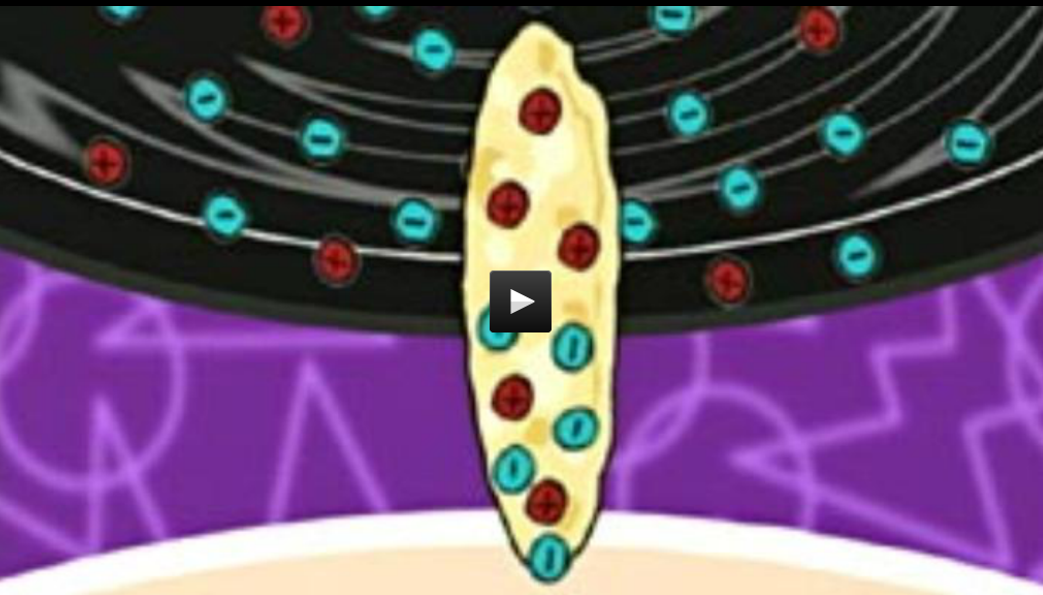
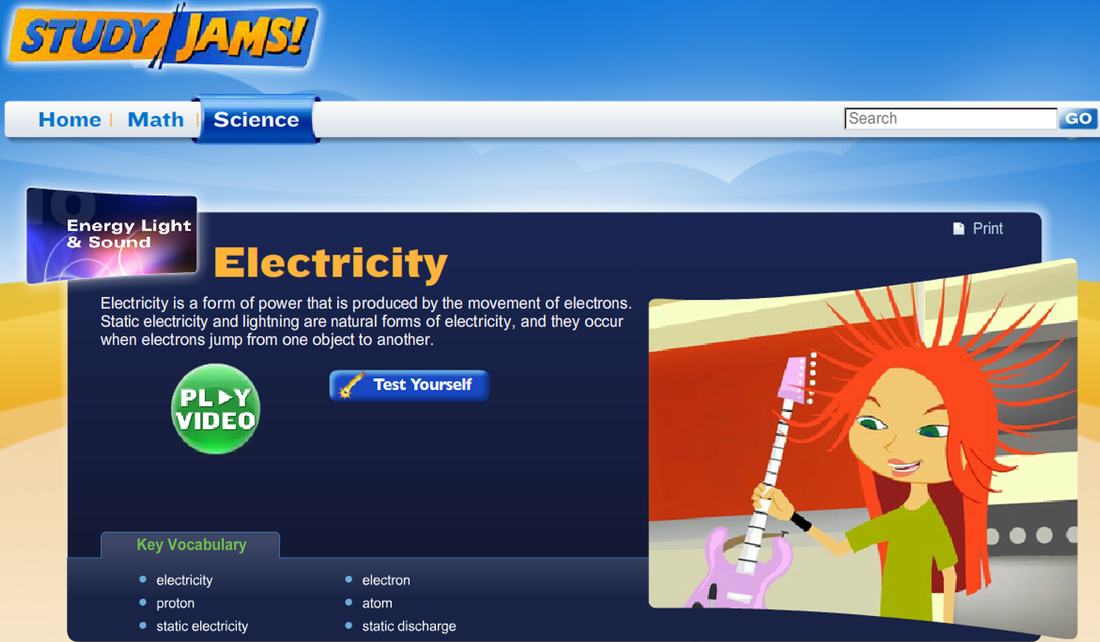
What causes static electricity? You experience the power of electricity every day. When you walk across the room, lean down to pick up your keys, then zap...a spark of electricity just shocked you. This spark is caused by the imbalance of positive and negative charges between the atoms of the two objects touching each other.
What causes static electricity? You experience the power of electricity every day. When you walk across the room, lean down to pick up your keys, then zap...a spark of electricity just shocked you. This spark is caused by the imbalance of positive and negative charges between the atoms of the two objects touching each other.
|
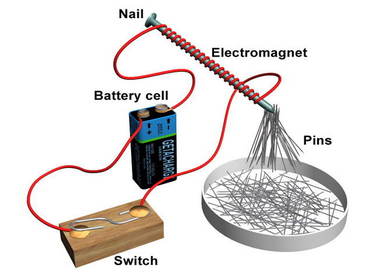
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by electric current ~usually a battery. The magnetic field disappears when the current of electricity is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. |
|
|
|
|

Core Standard: Provide evidence that heat and electricity are forms of energy. (4.1.1, 4.1.2)
Core Standard: Design and assemble electric circuits that provide a means of transferring energy from one form or place to another. (4.1.3, 4.1.4, 4.1.5)
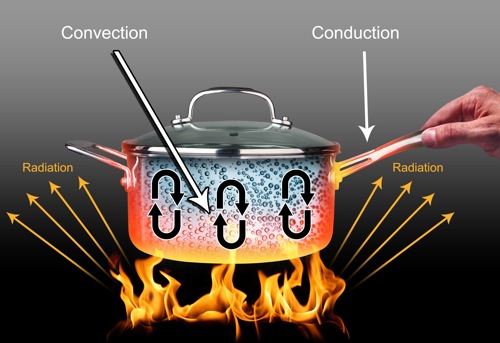
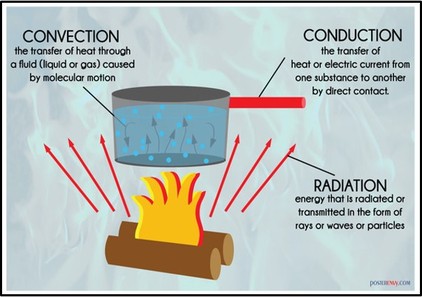
4.1.1 Describe and investigate the different ways in which heat can be generated.
4.1.2 Investigate the variety of ways in which heat can be generated and moved from one place to another. Explain the direction the heat moved.
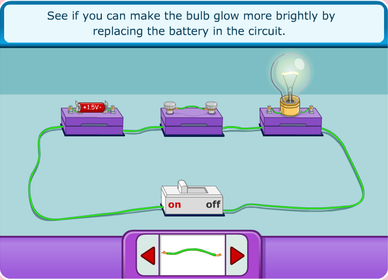
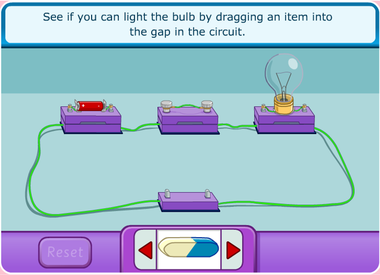
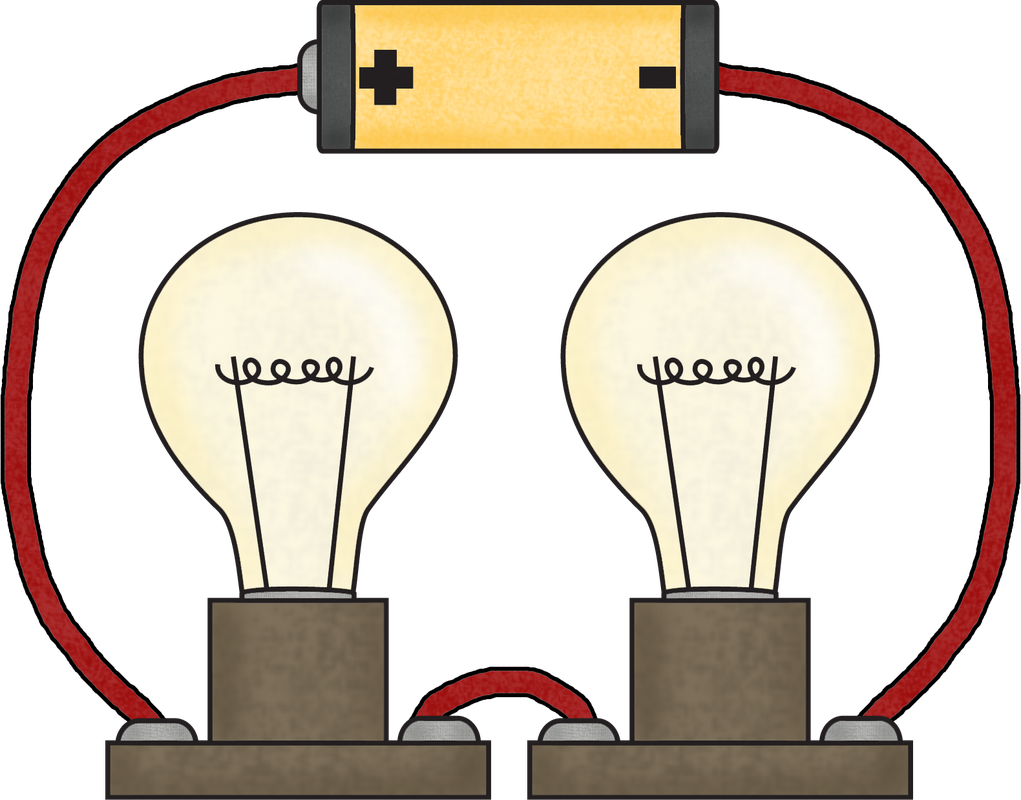
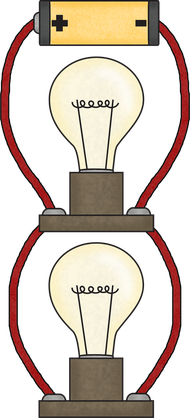
4.1.3 Construct a complete circuit through which an electrical current can pass as evidenced by the lighting of a bulb or ringing of a bell.
4.1.4 Experiment with materials to identify conductors and insulators of heat and electricity.
4.1.5 Demonstrate that electrical energy can be transformed into heat, light, and sound.
Core Standard: Design and assemble electric circuits that provide a means of transferring energy from one form or place to another. (4.1.3, 4.1.4, 4.1.5)
4.1.1 Describe and investigate the different ways in which heat can be generated.
4.1.2 Investigate the variety of ways in which heat can be generated and moved from one place to another. Explain the direction the heat moved.
4.1.3 Construct a complete circuit through which an electrical current can pass as evidenced by the lighting of a bulb or ringing of a bell.
4.1.4 Experiment with materials to identify conductors and insulators of heat and electricity.
4.1.5 Demonstrate that electrical energy can be transformed into heat, light, and sound.